In a dynamic information age of high technologies and continuous equipment modernization it is impossible to imagine any office, any company and any residential building without multipath cabling. It provides transfer of information data, television and sound broadcasting, fire safety and security systems. The key to trouble-free operation of any equipment is a structured cabling system. It is a whole complex of modular subsystems arranged in a hierarchical way.
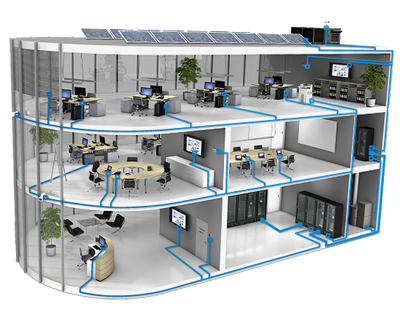
Structured cabling systems are an integral part of efficient operation of any equipment and have a number of undeniable advantages:
- Generality. Unified systems allow to connect both telephone network, and Internet, and broadcasting of any video or audio signals .
- Capability of configuration. When organizing new cable branch, there is no need to install a new system, it is enough to complement the main one with new functionality.
- Reliability. Structured cabling systems are arranged in such a manner to prevent property damage in the event of an accidental or emergency situation.
- Endurance. Upon condition of high-quality materials use and proper installation such systems can easily function for more than a decade.
Structured cabling system includes a set of specialized modules that perform individual functions. The system includes:
- Cable - is a fundamental component of the system; it performs direct transmission of information data. There can be applied shielded-type or unshielded-type cables. All wires of shielded cables are enclosed in a metal armoring that provides protection against noise interferences. Unshielded cables do not provide such protection.
- Socket - is a standard entry point to the cable network.
- Switchboard cords - are necessary for direct connection of office equipment or other equipment.
Up to date, there are two options for structured cabling system construction:
- method of hierarchical star;
- architecture of single-point control.
Each of the options has its own characteristics and features.
The architecture of hierarchical star has a complex structure of cross, but it differs by flexibility of system control and ensures maximum adaptation of new branches. It can be used both within a single building, and for a group of buildings.
Advantages of such systems:
- general flexibility, for the purposes of active equipment including;
- compliance with standards;
- ability to distribute equipment.
The architecture of single-point control is notable for simplicity of operation and provides direct connection of separate workplaces to the main cross, from which administration is carried out. Its advantages are as follows:
- possibility of centralized control;
- simple maintenance;
- compliance with standards for a total length of up to 100 m.

Structured cabling systems are multicomponent regardless of the type of architecture. Mandatory subsystems are horizontal, backbone, equipment and work location subsystems.
Horizontal subsystem - is a part of the overall telecommunication cabling system; in an ideal scenario such a subsystem should be individual for each floor. It passes between the work location connector and the horizontal cross, which is located in the telecommunications cabinet.
Backbone subsystem - is cable routing that connects horizontal and intermediate crosses with the main cross in the operating room. The backbone cable is laid in the form of a star, originates in the main cross and is routed to each telecommunication cabinet. This is the hierarchical star topology.
Work location subsystem - is a standard system that connects the socket directly to the working equipment (telephone, computer). An obligatory condition for arranging such a subsystem is a location of key points in the place of immediate access. Typically, the workplace is equipped minimum with two standard plug connections.
Equipment subsystem - is a module for authorized but collective access, it is a telecommunication cabinet that transmits the environment for telecommunication equipment. Such a subsystem should provide the necessary conditions for operation of passive equipment that is connected to it.
Condition for all subsystems that must be strictly observed is a high-quality grounding performed in accordance with accepted regulations and standards.
Innovative technologies gradually replace traditional methods in each sphere. Technical progress is rapidly moving forward, replacing obsolete methods. The same scenario is observed for the arrangement of cable systems. Traditional cable systems have a number of disadvantages: a weak level of reliability and durability, the complexity of installation, unreasonable overspendings, and dependence on the network technology used. That is why they were replaced by structured cabling systems, which surpass them in many respects:
- Integrity. A single system is used for multidirectional operation.
- Fair value. All costs are justified due to reliability and durability of functioning.
- Combinativity. It is possible to combine copper and fiber optic cables.
- Commonality. Standard materials are used for installation.
- Flexibility. Sockets are used to connect any equipment, there is no dependence on any technology or equipment supplier.
The efficiency of work is caused by correct organization of the structured cabling system. Often the companies are trying to install such systems independently to save money without having the relevant experience and acting blindly. Such actions can not only be ineffective but also result in complex emergency situations leading to damage to expensive property and sometimes to injuries. It must always be remembered that such systems are to meet special regulations and standards.
Installation of a structured cabling system is a highly complex process requiring not only qualitative materials of certain specifications but also test equipment, tools and documentary certification of such a system. It is more expedient to involve an integrator company in this work. Usually such companies have an arsenal of the necessary tools and a staff of specialists with relevant knowledge and experience in this field. The main criteria for choosing such a company are as follows:
- Good reputation and successful experience in such services rendering.
- Fair pricing and licensing for such work.
- Use of high-quality materials and granting of guarantees.
- A packaged approach, rendering of a full range of services and timely maintenance.
Only upon availability of such aggregate characteristics the company will be able to perform all the work qualitatively.
| Usual name | ISO/IEC indication 11801 | Overall shield | Individual shield |
| UTP | U/UTP | N/A | N/A |
| STP, ScTP, PiMF | U/FTP | N/A | foil |
| FTP, STP, ScTP | F/UTP | foil | N/A |
| STP, ScTP | S/UTP | braid | N/A |
| SFTP, S-FTP, STP | SF/UTP | braid, foil | N/A |
| FFTP | F/FTP | foil | foil |
| SSTP, SFTP, STP PiMF | S/FTP | braid | foil |
| SSTP, SFTP | SF/FTP | braid, foil | foil |
| Category | Band width, MHz | Application | Notes |
| 3 | 16 | 10BASE-T, 100BASE-T4 Ethernet | 4-pair cable, is used for construction of telephone and local 10BASE-T and token ring networks, supports data transfer rates of up to 10 Mbit/s or 100 Mbit/s using 100BASE-T4 technology within a distance of 100 meters. In contrast to the previous two it meets the requirements of the IEEE 802.3 standard. Now it is used mainly for telephone lines. |
| 5e | 100 | Fast Ethernet (100BASE-TX), Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) | 4-pair cable, upgraded category 5 (refined / improved specifications). Data transfer rate is up to 100 Mbit/s when using 2 pairs and up to 1000 Mbit/s when using 4 pairs. 5e cable category is the most common and is used for computer networking. Sometimes there is a two-pair cable of 5e category. The advantages of this cable are the lower cost and the lesser thickness. |
| 6A | 500 | 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GBASE-T) | consists of 4 pairs of conductors and is able to transfer data at rates up to 10 Gb/s at distances up to 100 meters. It was added to the standard in February 2008, ISO / IEC 11801: 2002 amendment 2. The cable of this category has either overall (F / UTP) or individual shields (U / FTP). |



